
Yoga is very ancient practice method originated in India, which for centuries has been legendary. Yoga is a philosophy of truth which is not limited to India but for the whole mankind.
Those who practiced yoga was called as Yogis, these Yogis believed that a man in order to be in harmony within the self and his environment he has to integrate the bod, mind and spirit. For these to be integrated, Yogis formulated a way to achieve and maintain balance through physical training, breathing methods and mental focus which is known as Asana, Pranayama and Meditation, which are the three structures of Yoga.
Yoga is a word derived from the Sanskrit word "Yuj" which means unite, merge or join. " युज्यते अनेन इति योग: l "
Yoga is that which joins. In the traditional terminology, it is joining of the individual self, जीवात्मा with the Universal Self, परमात्मा.
In this context the word Yoga is a process of integrating body, mind and spirit.
Every aspects of human life skills is practice, One who have attained self-realization and achieved the enlightened relationship with supreme conscious are called as Yogis and these Yogis have expressed definitions of Yoga in their own views and experience emphasized on physical, mental, emotional, social and spiritual training to attain enlightenment and connect to the cosmic energy.
" योग: चित्त वृत्ति निरोध: l "
Controlling over the whirlpool of mind stuff is Yoga.
- Maharshi Patanjali
" योग: कर्मसु कौशलम् l "
Yoga is skill in action.
- Bhagavatgeeta
" मन: प्रशमन उपाय: योग इत्यभिधीयते l "
Yoga is called a skilful trick to calm down the mind. It is an Upayah, a skillful subtle process and not a brutal, mechanical gross effort to stop the thoughts in the mind.
- Yoga Vasishta
" समत्वं योग उच्यते l "
Evenness is verily Yoga.
- Bhagavatgeeta
" Mastery over the mind is Yoga " - Swami Vivekananda
" Yoga deals with the Physical, Mental and Spiritual wellbeing of an individual " - B. K. S. Iyangar
" Yoga is the practice of tolerating the consequences of being Yousef " - Bhagavatgeeta
" The Attitude of Gratitude is the Highest Yoga " - Yogi Bhajan

Pre vedic period is a period before the aryan invansion on indian subcontinent. Pre vedic times were times when there is no caste based system followed, all shared equal rights & only worship of one god Rudra(shiva).
Since ancient time Indian philosophy has focused over the fundamental questions of existence: What is the world? If it's a creation, what are its constituents ? Who is the creator? What is life ? What is 'truth' ? What is 'the nature of reality'? so some people stayed away from the material society went isolated in the forest and meditated on these fundamental questions, What was revealed to them was expressed in hymns consistuted the Vedas (Knowledge) and the Upanishads.
These collection are grouped as four Vedas Namely

This covers an extensive period of approximately 2000 years until the second century. Gnostic texts called the Upanishads that spoke in detail about the self and ultimate reality. The term 'Upanishad' literally neans "sitting down near or close to", which implies listening closely to the mystic doctrines of a guru, which was orally transmitted about the fundamental truths of the universe. Which this tradition was called as Guru Shishya Parampara in the forest Ashrams or Hermitages.
The approximately 200 Upanishads. One of the most remarkable yoga scriptures is the Bhagvadgeeta, which was composed around 500 B.C. contains 18 Chapter and speaks about ultimate truth through four fold yoga or Streams of Yoga.
Different yogis have different yoga as a skills of life in there prominent aspects Which one can attain his destination through specific ways or marga. So the path of yoga csn be classified into four streams of Yoga.
The Great sages worked on the principal based on Vedas and devoted six schools of Vedic Philosophies known as Sad Darshana. All six schools of Vedic Philosophy Aim to describe following three key features.
Nature Of External World And It's Relationship With Individual Soul.
Relationship of World Of Appearance To Ultimate Reality.
Describing The Goal Of Life And Means By Which One Can Attain The Goal.
Sad Darshana Are :

This is the period where yoga took it's systematic principles. Maharshi Patanjali who is rightly called as father of Yoga who codified yoga into systemstic practice in his 196 yoga aphorisms which was orderly classified into four verses such as :
Ashtanga Yoga or Eight fold path of practice method from Sadhana Pada is so authenticated teachings for yoga practitioner even today.
Ashtanga Yoga is also called as Raja Yoga. The eight fold paths of Ashtanga Yoga are :
Are physical training for Healthy and Decease less, main two factors are 'to be firm & comfort' because physical body is the matter for subtle energy to exist.
Harmonizing the normal breathing system to calm down the mind distractions and activating the spiritual conscious within.
Practice of destroying the external temptation if mind caused by sensory systems and redirecting the mind thoughts inward. Pratyahara is the bridge between Antaranga and Bahiranga Yog.
Practice followed by Pratyahara to continues concentration of mental waves to one particular subject with effort is Dharana.
The intense level of Dharana leads to effortless stilling of mind in particular state of conscious.
The ultimate union with supreme self, the state of eternal bliss.
In this period Practice of Yoga took a different development. In the early times yogis emphasized more on meditation and contemplation with moral principle methods to attain the infinite self, but during these period yogis realised about The Spiritual energies latent in an individual physical body which has to be rejuvenated by physical discipline and then follow the remaining paths.
It is the Hatha Yoga which "Ha" means ida and "tha" means pingala are the two energy channels, harmonizing the vital energy through these channels to activate the latent spiritual energy called as "Kundalini Shakti" which is known as dormant serpent power Situated at the base of the spine in the physical body, By activating Kundalini energy raises upward in the line of spine from the bottom activating latent spiritual energy centers called Chakras.

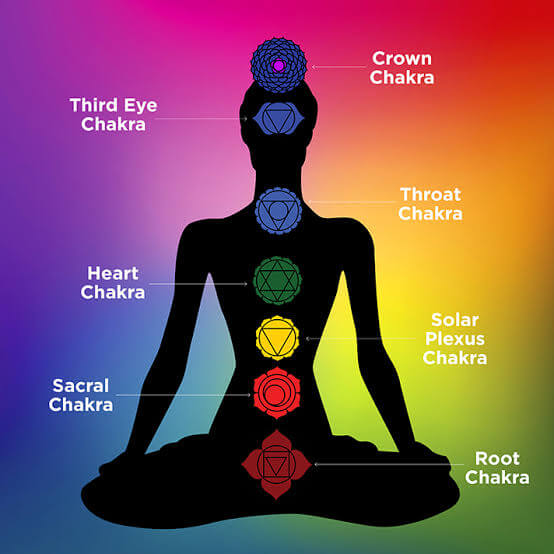
By activating these six Chakras one will achieve the ultimate union at Sahasrara Chakra the seventh chakra opens up at the crown of the head.
During this period combination of Ashtanga Yoga and Hatha Yoga principles came into practice. Yoga tradition developed at two stages, In the beginning of modern age tradition of yoga started spreading out of India. This period was around late 1800s and early 1900s, Philosophy of yoga started spreading round the world by some of the great Indian yogis like Swami Vivekananda, Swami Shivananda Saraswati, B.K.S. Iyangar, Pattabijois and many more. During this time great yogi T. Krishnamacharya who strongly promoted Hatha Yoga practice vin India producted three students B.K.S. Iyangar, Pattabijois and T.K.V. Desikachar who would continue his legacy in and out of India especially western countries were attracted to intense Asana practices of Hatha Yoga.
Many practitioners from different physical activities are also influenced by yoga asanas and have blended with their physical activities to experience deeper awareness.
Here are some popular styles of Yoga practice like